In this Lab I have learn about "gcc" compiler options to optimize C code.
To begging lets use following 3 compile options.
is to enable debugging information.
to tell compiler which level of optimization to apply on Code. (Capital letter and then digit Zero).
is to tell compiler to not use built in function optimization. We will look in a bit.
We will be adding and removing the compile option to compare some factors like code size, sections in assembly .
1. Lets compile the following basic Hello World code.
Compile Argument : gcc -g -O0 -fno-builtin hello.c
From above compile , the executable file size was 11K.
To see the compiled object assembly code, I used objdump -d | less. This command will dump executable file in less so, we can see the output .
Above snippet is how main function looks like in assembly .
2. Second step is to add the -static option in compile option.
Compile Argument : gcc -g -O0 -fno-builtin -static hello.c
Q:What happens when we use static option while compile?
A: It tells the compiler to load assembly for the whole library used by the program.
So when program runs, it doesn't have to go through link table to find the function in library.
This can improve performance but executable size will increase a lot.
On this compile file size jumped to 895K.
From the snippet below , there are two new lines added at the end of the main section.
These are padding so that program instructions can end at a particular memory boundary.
3. Third step , compile without the -fno-builtin
Compile Argument : gcc -g -O0 -static hello.c
-fno-builtin asks the compiler not to do any optimization for built in functions, in our case printf.
If we remove -fno-builtin from compile, then compiler will optimize the printf .
After the objdump , if we look at the function call for printing in the section main, it is changed to <_IO_puts>
4. Removing the compiler option -g .
Compile Argument : gcc -O0 -fno-builtin hello.c
Now lets compare the object with the gcc -g -O0 -fno-builtin hello.c ( First step ).
1. Code size reduced by 20% (9K)
2. From objdump ,sections like .debug_line, .debug_str, .debug_abbrev , .debug_aranges,.debug_info are removed.
Debugging Section Headers.
1. debug_info : describes the program's debug information for ensuring simple data types, variables and function are being used correctly.
2. debug_types : ensuring complex data types, like arrays, list, struct are being uses correctly
3. debug_str section: contains strings that are used more than once.
5. Some Optimization level
| Option |
Optimization Level |
execution time |
code size |
memory usage |
compile time |
| -O0 |
optimization for compilation time (default) |
+ |
+ |
- |
- |
| -O1 or -O |
optimization for code size and execution time |
- |
- |
+ |
+ |
| -O2 |
optimization more for code size and execution time |
-- |
|
+ |
++ |
| -O3 |
optimization more for code size and execution time |
--- |
|
+ |
+++ |
| -Os |
optimization for code size |
|
-- |
|
++ |
| -Ofast |
O3 with fast none accurate math calculations |
--- |
|
+ |
+++ |
+increase, ++increase more, +++increase even more. -reduce ,--reduce more, ---reduce even more
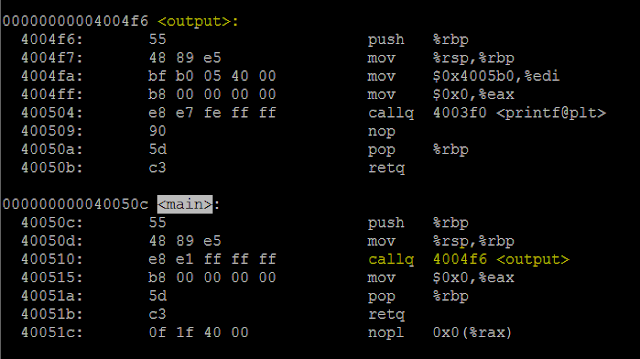
7. Calling printf within a method.
This section , we will create the function output() with printf inside. And, call output function from main(). Code looks like following snippet.
Compile Argument :
gcc -O0 -fno-builtin hello.c
Now,objdump that executable and one can see new section is being created for the output function.
So, new section will be created for each method.
We have seen , optimization , assembly section and function call. There are lot more options for gcc compiler if you look at the man page. Some option may improve performance of program but the executable size would be bigger and for other options is completely opposite. These days, programmers dont have to think about writing code in optimized way because compiler can do it for them . However, Algorithm , approach and some other factors which still depends on programmer.